C++
2024.02.27 - 구조체(struct)
강병곤
2024. 2. 27. 17:33
구조체는 여러가지 변수를 묶어서 하나의 데이터로 정리할 때 사용할 수 있는 사용자 정의 자료형이다.
- 구조체 만들기
예시) 학생에 대한 여러가지 정보를 멤버 변수로 가진 Student라는 이름의 구조체
#include<iostream>
struct Student{
std::string name;
int age;
int height;
};
- 구조체 변수 만들기, 사용하기
예시)
#include<iostream>
struct Student{
std::string name;
int age;
int height;
};
int main(){
Student std1;
std1.name = "홍길동";
std1.age = 15;
std1.height = 180;
/*
Student std1 = {"홍길동", 15, 180};
이렇게 구조체 변수를 초기화 할 수도 있다.
*/
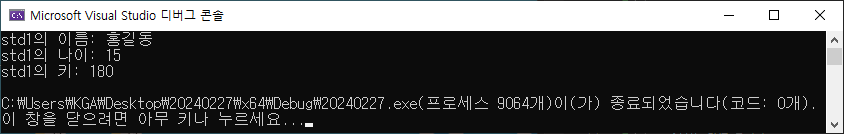
std::cout << "std1의 이름: " << std1.name << std::endl;
std::cout << "std1의 나이: " << std1.age << std::endl;
std::cout << "std1의 키: " << std1.height << std::endl;
}
- 구조체 멤버 함수 만들고 사용해보기
구조체에는 멤버 변수 뿐만 아니라 멤버 함수가 들어갈 수 있다. 다음은 멤버 함수를 만들고 사용해보는 예제이다.
예시)
#include<iostream>
struct Student{
std::string name;
int age;
void Print();
};
int main(){
Student stdnt;
stdnt.Print();
}
void Student::Print(){
std::cout << "나는 Student 구조체 안의 Print()함수";
}
- 구조체 자료형으로 배열 만들어 보기
예시)
#include<iostream>
struct Student {
std::string name;
int age;
int height;
};
int main() {
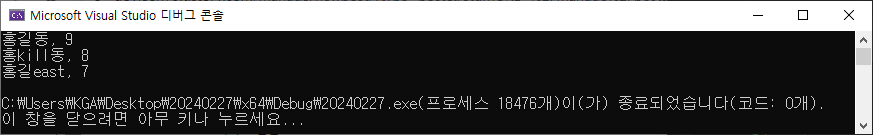
Student sd[3] = { { "홍길동", 9 }, { "홍kill동", 8 }, { "홍길east", 7 } };
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
std::cout << sd[i].name << ", " << sd[i].age << std::endl;
}
}
- 구조체를 매개변수로 받고 구조체를 return하는 함수
예시)
#include<iostream>
struct Zerg {
int hp;
int atk;
int speed;
};
Zerg LvUp(Zerg lv);
int main(){
Zerg zergling = { 100, 20, 5 };
zergling = LvUp(zergling);
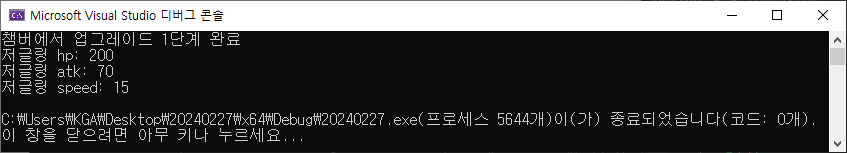
std::cout << "챔버에서 업그레이드 1단계 완료" << std::endl;
std::cout << "저글링 hp: " << zergling.hp << std::endl;
std::cout << "저글링 atk: " << zergling.atk << std::endl;
std::cout << "저글링 speed: " << zergling.speed << std::endl;
}
Zerg LvUp(Zerg lv){
lv.hp += 100;
lv.atk += 50;
lv.speed += 10;
return lv;
}